check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
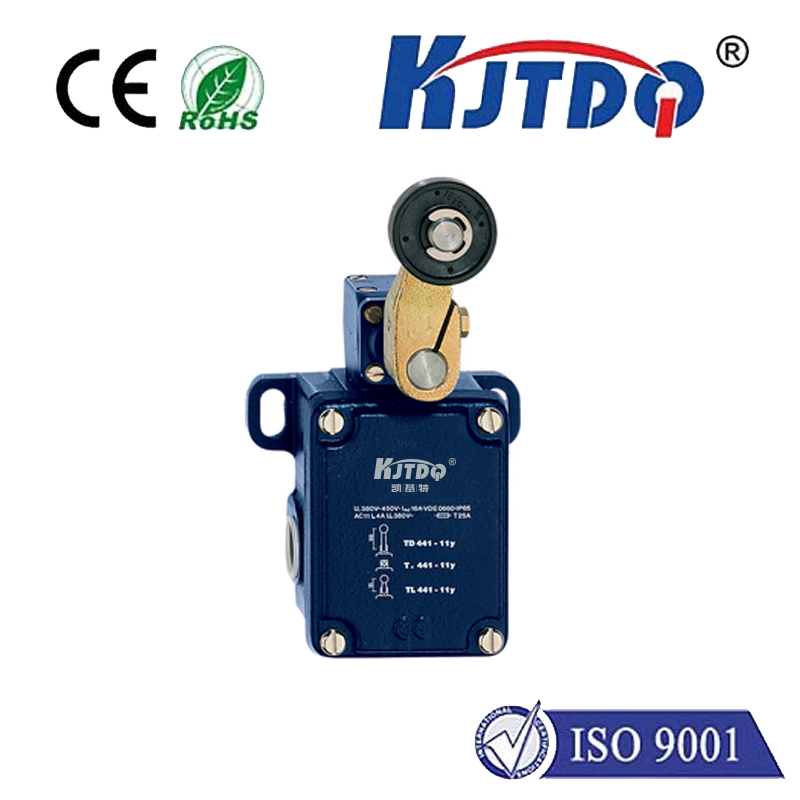
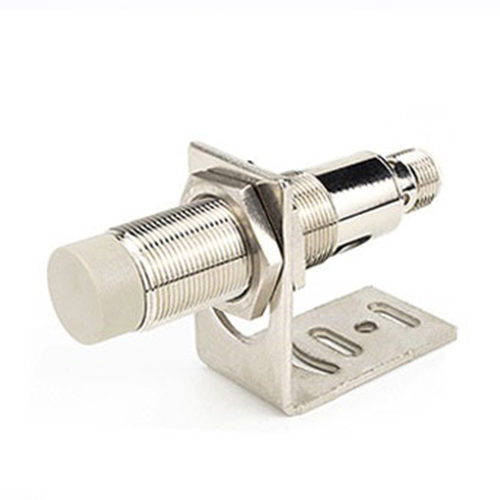
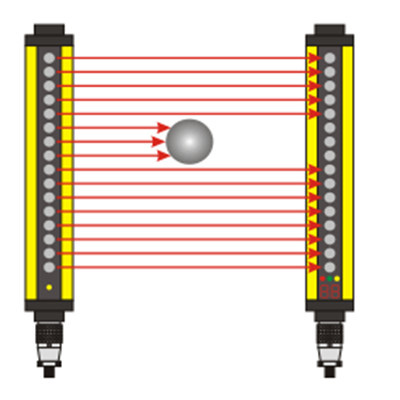
In today's fast-paced technological landscape, the demand for precision measurement has never been greater. From autonomous vehicles navigating city streets to advanced robotics in manufacturing, the ability to accurately gauge distance is a fundamental requirement. This is where the accurate rangefinder sensor steps into the spotlight, serving as a critical component that bridges the gap between digital intent and physical action. Unlike traditional measurement tools, modern rangefinder sensors utilize sophisticated principles like time-of-flight (ToF), phase-shift analysis, or laser triangulation to deliver data with remarkable fidelity. The core value of an accurate rangefinder sensor lies in its consistency and reliability. Even in challenging environmental conditions—such as low light, adverse weather, or cluttered backgrounds—these sensors are engineered to maintain their performance. This resilience is achieved through advanced signal processing algorithms that filter out noise and interference, ensuring that the distance reading reflects the true position of the target object. For industries like construction and surveying, this translates to faster project timelines and reduced material waste, as measurements can be trusted implicitly from the first reading.
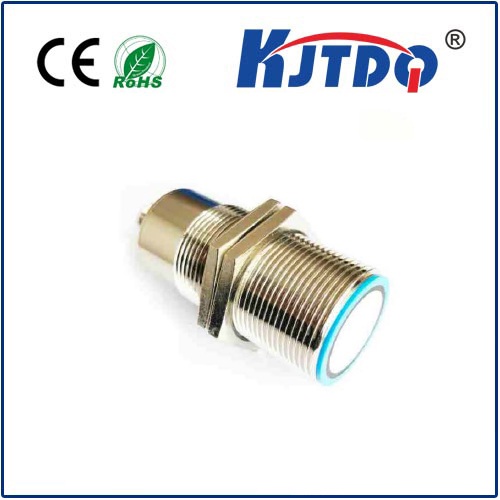
The integration of accurate rangefinder sensors into consumer electronics has quietly revolutionized user experiences. Smartphones employ these sensors to enable faster and more reliable autofocus in cameras, capturing crisp images instantaneously. In home automation systems, they facilitate intuitive gesture controls and enhance the safety of smart appliances by detecting the presence of individuals or objects. The development of compact, low-power sensor modules has been a key driver in this proliferation, allowing designers to incorporate precise ranging capabilities without sacrificing device form factor or battery life. Looking forward, the evolution of accurate rangefinder technology is closely tied to advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning. By feeding high-fidelity distance data into AI models, systems can achieve a more nuanced understanding of their surroundings. This synergy is particularly evident in emerging fields like augmented reality, where an accurate rangefinder sensor helps seamlessly blend digital overlays with the real world, and in logistics, where it optimizes warehouse automation by precisely tracking inventory movement. The ongoing refinement of sensor materials and optical components promises even greater accuracy over longer ranges, paving the way for next-generation applications that we are only beginning to imagine.