check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
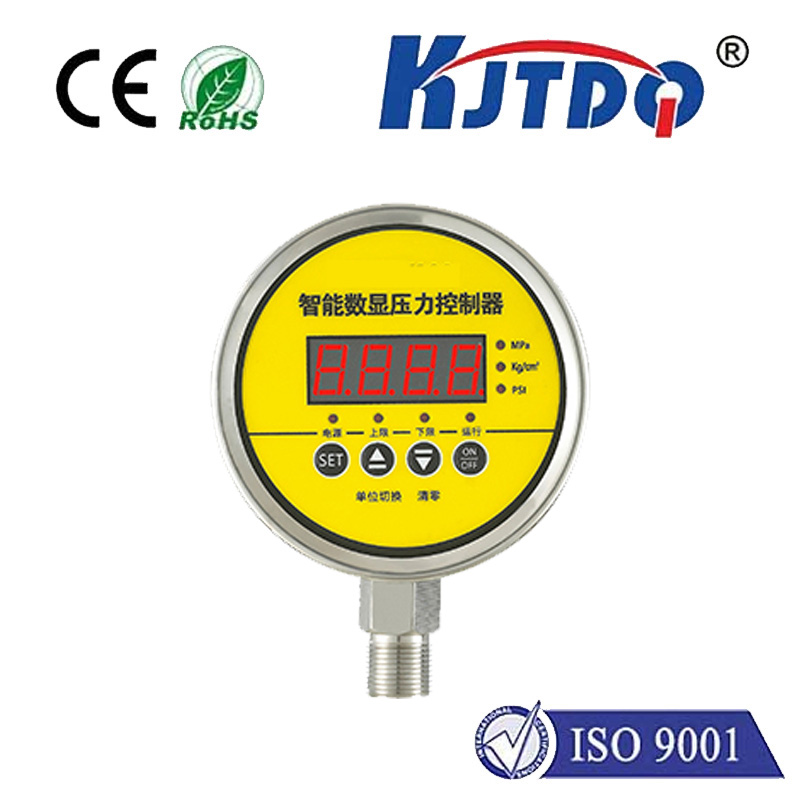
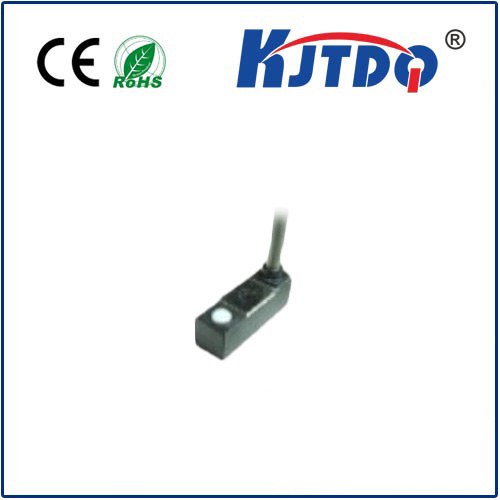
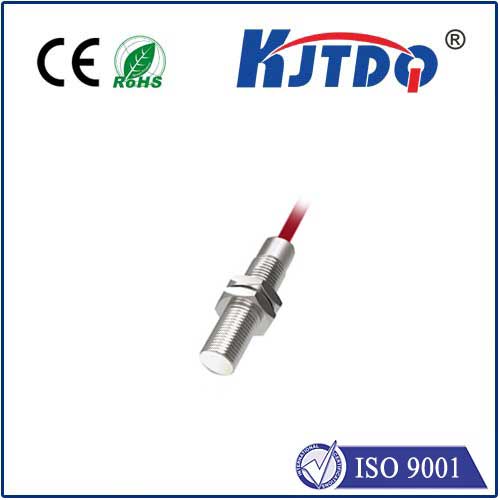
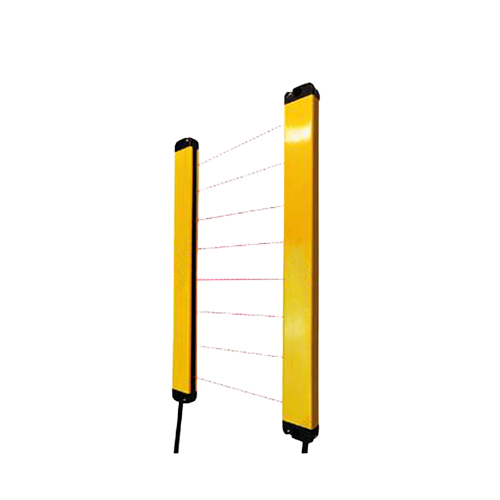
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronic sensing, the proximity IR sensor stands as a cornerstone technology, enabling devices to perceive their environment without physical contact. The fundamental principle relies on infrared light emission and reception. An IR LED emits an infrared beam, which, upon encountering an object, reflects back to a photodiode or similar receiver. The sensor's circuitry then analyzes the reflected signal to determine the presence, absence, or distance of the object. This simple yet powerful mechanism forms the basis for countless applications where touchless interaction, object detection, or distance measurement is paramount.
The integration of advanced components like the KJTDQ module has significantly elevated the performance benchmarks for these sensors. Such modules are engineered for heightened sensitivity and stability, often incorporating noise-filtering algorithms and ambient light rejection techniques. This ensures reliable operation even in challenging conditions with variable lighting or potential signal interference. The result is a sensor that delivers consistent, accurate readings, which is critical for applications demanding high precision.
One of the most visible applications is in the consumer electronics sector. Smartphones and tablets utilize proximity IR sensors to deactivate touchscreens during calls, preventing accidental inputs from cheek contact. Similarly, automatic faucets, soap dispensers, and hand dryers in public restrooms rely on these sensors for hygienic, hands-free operation, conserving resources by activating only when needed. In the realm of robotics and automation, proximity IR sensors are indispensable for obstacle avoidance and navigation. Autonomous mobile robots, robotic arms in assembly lines, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) use arrays of these sensors to map their immediate surroundings, detect unexpected obstacles, and adjust their path in real-time, ensuring safe and efficient movement.
The automotive industry is another major beneficiary. Proximity IR sensors are integral to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), contributing to features like blind-spot monitoring, parking assistance, and collision warning systems. They help in detecting vehicles, pedestrians, or objects in close proximity to the car, providing crucial data to the vehicle's computer to alert the driver or initiate automatic braking. In industrial settings, they are deployed for object counting on conveyor belts, liquid level detection in tanks, and ensuring proper positioning of components in manufacturing processes, thereby enhancing productivity and safety.
Looking toward the future, the role of proximity IR sensors is set to expand further with the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart infrastructure. In smart homes, they can contribute to energy efficiency by controlling lighting and HVAC systems based on room occupancy. In smart cities, they could monitor traffic flow or parking space occupancy. The ongoing miniaturization of components and reduction in power consumption, as seen in advanced modules like the KJTDQ, will enable their integration into even smaller, battery-powered wearable devices and embedded systems.
Selecting the right proximity IR sensor requires careful consideration of several parameters. The sensing range, response time, and output type (digital or analog) must align with the application's requirements. Environmental factors such as operating temperature, potential exposure to dust or moisture, and the material and color of the target objects (as different surfaces reflect IR light differently) are also critical. High-quality modules address these challenges through robust design and intelligent signal processing.
In conclusion, the proximity IR sensor, particularly when enhanced by sophisticated components, is a transformative technology that bridges the physical and digital worlds. From simplifying daily interactions with consumer gadgets to ensuring precision and safety in complex industrial and automotive systems, its impact is profound and pervasive. As technology continues its forward march, the evolution of these sensors will undoubtedly unlock new possibilities, making our interactions with machines more intuitive, efficient, and seamless than ever before.