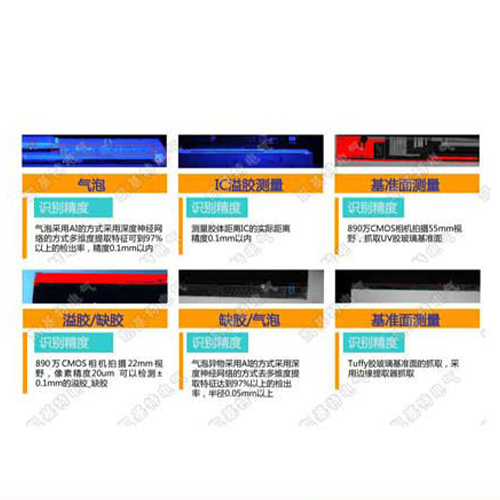
check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
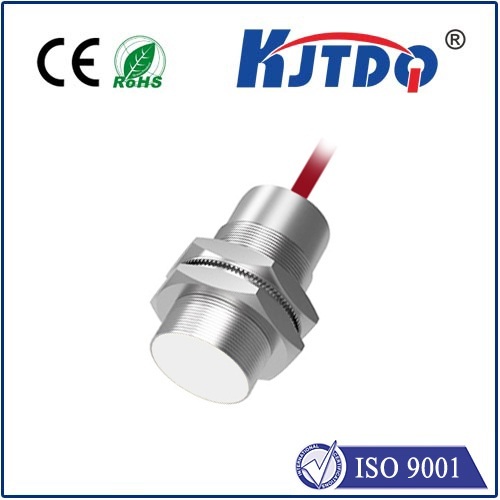
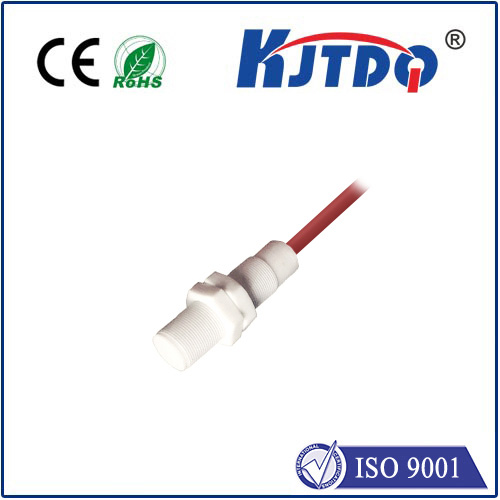
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation and smart systems, the infrared photoelectric sensor stands as a cornerstone technology, enabling precise, non-contact detection across countless applications. Unlike traditional mechanical switches or basic sensors, these devices utilize infrared light to detect the presence, absence, or distance of objects with remarkable accuracy and reliability. The core principle involves an emitter that projects an infrared beam and a receiver that captures the reflected or interrupted signal. This simple yet powerful mechanism allows for operations in challenging environments where dirt, dust, or varying light conditions might hinder other sensing methods.
The versatility of infrared photoelectric sensors is truly staggering. In manufacturing and packaging lines, they ensure products are correctly positioned, counted, and sorted, significantly reducing errors and boosting efficiency. Within the realm of security, they form the invisible backbone of intrusion detection systems, creating protective beams that trigger alarms when crossed. Automotive industries rely on them for assembly line automation and safety features, while consumer electronics integrate these sensors for touchless interfaces and power-saving functions. Their ability to function without physical contact eliminates wear and tear, granting them a exceptionally long operational life and minimal maintenance requirements.
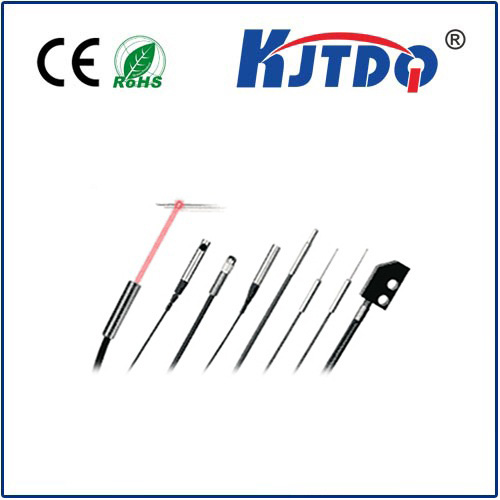
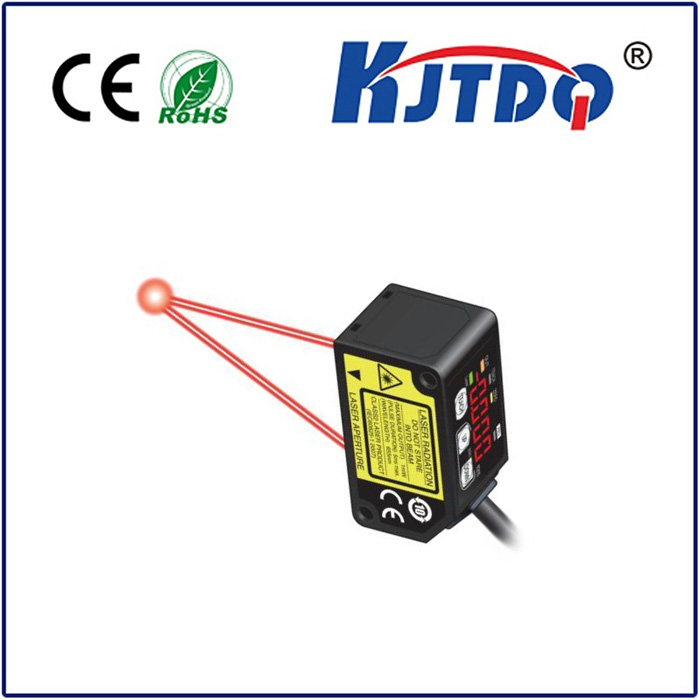
When selecting an infrared photoelectric sensor, several key specifications demand attention. Sensing range, response time, and output type (such as NPN, PNP, or analog) are critical parameters that must align with the application's needs. Environmental factors like ambient temperature, potential exposure to chemicals, and required ingress protection (IP) ratings are equally important to ensure consistent performance. Modern advancements have led to the development of background suppression models, which can ignore reflections from distant surfaces, and fiber-optic variants that allow sensing in extremely confined or hostile spaces.
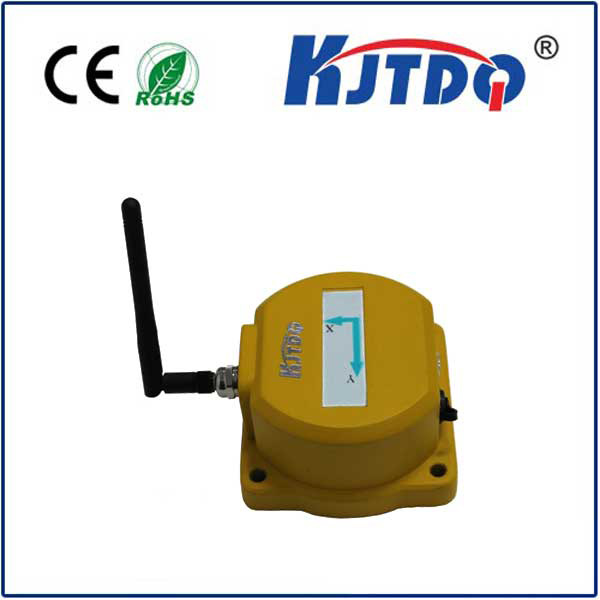
The integration of infrared photoelectric sensors into the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 frameworks represents the next frontier. Smart sensors now come equipped with digital communication protocols like IO-Link, providing not just a detection signal but also diagnostic data on device health, temperature, and signal strength. This predictive maintenance capability prevents unexpected downtime and optimizes entire production processes. The KJTDQ series, in particular, exemplifies this trend, offering enhanced noise immunity, adjustable sensitivity, and robust housings designed for the most demanding industrial settings.
Despite their robustness, optimal performance hinges on correct installation and alignment. Ensuring a stable mounting, avoiding optical interference from other light sources, and regularly cleaning the lens are simple yet vital practices. As technology progresses, we can anticipate sensors with even longer ranges, higher precision, and lower power consumption, further solidifying their indispensable role in building smarter, more responsive automated systems. From humble beginnings to becoming a critical component in robotics, smart agriculture, and energy management, the infrared photoelectric sensor continues to illuminate the path toward greater innovation and efficiency.