check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
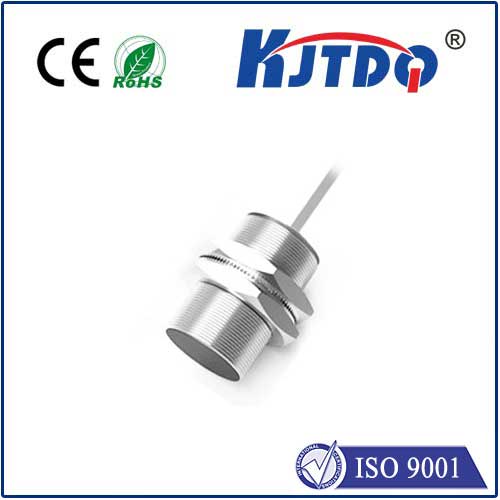
In the world of industrial automation, precision and reliability are non-negotiable. Among the myriad of sensors available, the retro-reflective photoelectric sensor stands out as a versatile and robust solution for countless detection tasks. Unlike through-beam sensors that require separate emitter and receiver units, or diffuse sensors that rely on the target's reflectivity, the retro-reflective photoelectric sensor combines the emitter and receiver in a single housing. It projects a light beam towards a specialized reflector, which bounces the beam directly back to the receiver. When an object interrupts this beam, the sensor triggers a detection signal. This ingenious design offers a perfect balance of long sensing range, easy alignment, and consistent performance, making it a cornerstone technology in modern manufacturing, packaging, and material handling systems.
The core advantage of the retro-reflective photoelectric sensor lies in its operational principle. The dedicated reflector, often a corner-cube prism, is engineered to return the light beam along a path parallel to its incoming direction, even if the alignment is not perfectly square. This characteristic provides a significant tolerance for mounting misalignment, reducing installation time and maintenance headaches. For applications where through-beam sensors are impractical due to space constraints or wiring complexity on both sides of the detection point, the retro-reflective type offers a compelling alternative with a comparable range. They are exceptionally effective for detecting transparent objects, such as glass or clear plastic bottles, which might be invisible to standard diffuse sensors. By using polarized light filters, advanced models can distinguish between the genuine reflection from the retro-reflector and false signals from shiny objects, a feature known as polarization discrimination.
Selecting the right retro-reflective photoelectric sensor requires careful consideration of several key parameters. The sensing range is paramount; it must comfortably exceed the actual distance to the reflector in your application, accounting for potential environmental factors like dust or vibration. The light source is another critical choice. Red LED light is common and cost-effective for general purposes, while laser models provide a highly focused beam for detecting very small objects or achieving precise positioning. For environments with high ambient light, infrared LEDs might be preferable. The output type—whether NPN, PNP, or relay—must be compatible with your control system (PLC). Furthermore, the housing material, typically stainless steel or rugged plastic, must withstand the specific industrial environment, including exposure to oils, coolants, or washdown procedures.
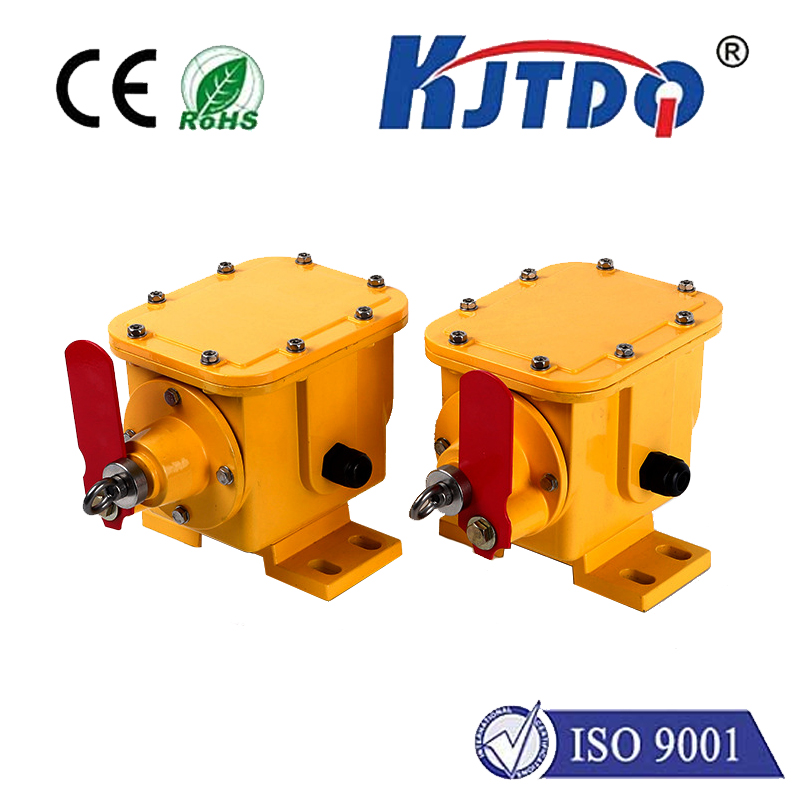
Real-world applications for these sensors are vast and varied. In conveyor systems, they are workhorses for detecting the presence of boxes, totes, or products, controlling stop/start functions, and counting items. Within automated packaging machinery, they ensure labels are present, verify fill levels, and confirm case sealing. In the automotive industry, they are used for robot guidance, part verification on assembly lines, and door or hatch positioning. Their ability to detect transparent materials makes them indispensable in bottling plants and pharmaceutical packaging lines. Even in harsh outdoor settings, such as vehicle access gates or parking lot systems, ruggedized retro-reflective sensors reliably detect vehicles by interrupting the beam to a reflector post.
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, proper installation and maintenance are crucial. Always secure the sensor and reflector firmly to minimize vibration-induced misalignment. Keep the lens and reflector surface clean from dirt, dust, and condensation, as contamination is the leading cause of failure. Regularly verify the alignment, especially after any maintenance on the surrounding machinery. Many modern sensors feature built-in diagnostic LEDs that indicate power status, output activation, and signal strength, providing immediate visual feedback for troubleshooting. When a sensor malfunctions, a systematic approach—checking power supply, inspecting for physical damage, cleaning optics, and verifying alignment—will resolve most issues quickly.
As technology advances, retro-reflective photoelectric sensors continue to evolve. Integration with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms is becoming more common, allowing for predictive maintenance by monitoring signal strength trends over time. Enhanced connectivity via IO-Link provides detailed parameter setting and diagnostic data directly to the control system. The development of background suppression techniques within the retro-reflective model itself further refines its ability to ignore distant objects beyond the reflector. For engineers and system integrators, understanding the capabilities and correct application of these sensors is fundamental to building efficient, fault-resistant automated systems. By choosing a high-quality retro-reflective photoelectric sensor and implementing it correctly, you invest in a detection solution that delivers unwavering reliability, reduces downtime, and safeguards your production process.