check

check

check

check
Imagine a factory floor humming with activity—robots assembling products, conveyors moving parts, and all of it running smoothly without a hitch. At the heart of this seamless operation lies a tiny but mighty device: the proximity sensor. Specifically, the 24V PNP proximity sensor is a cornerstone of modern automation, offering reliable, non-contact detection for countless applications. If you’re in the industrial sector, understanding this sensor isn’t just helpful—it’s essential for boosting efficiency and reducing downtime. In this article, we’ll demystify how these sensors work, why they dominate settings from manufacturing to automotive, and what makes them a smart choice for your projects. Let’s explore the core principles and practical insights you need.
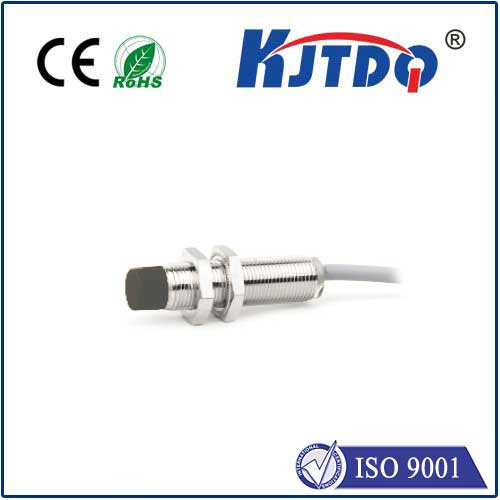
What is a Proximity Sensor and Why Does It Matter? Proximity sensors are electronic devices that detect the presence or absence of nearby objects without physical contact. They achieve this through electromagnetic fields or other technologies, making them ideal for environments where wear and tear or contamination are concerns. For instance, in a bottling plant, they ensure labels are applied correctly by sensing containers as they pass by. The 24V PNP proximity sensor elevates this concept with its unique design: it operates at a 24-volt DC power supply, which is a widely adopted standard in industrial systems for its balance of safety and performance, and uses a PNP (positive-negative-positive) transistor configuration. This means when the sensor detects an object, it outputs a positive voltage signal, simplifying integration with control systems like PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers).
How 24V PNP Proximity Sensors Work: Breaking Down the Basics At its core, a PNP proximity sensor functions by generating an electromagnetic field around its sensing face. When a metallic or non-metallic object enters this field—say, a gear on a production line—it disrupts the field, triggering the sensor’s internal circuitry. The PNP aspect refers to the transistor output: when activated, it “sources” a positive signal to the connected device, such as a relay or controller. This contrasts with NPN types, which “sink” the current and can be less intuitive in certain setups.
The 24V operating voltage is a key factor in its reliability. Why 24V? In industrial automation, this voltage level strikes a perfect balance: it’s high enough to overcome electrical noise and voltage drops in long cable runs (common in factories), yet low enough to ensure operator safety. For example, in automotive assembly, sensors running on 24V can detect car parts accurately even amidst electromagnetic interference from motors. Most industrial standards, like those from IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), recommend 24V for control circuits, making these sensors plug-and-play in existing systems.

Key Applications of 24V PNP Proximity Sensors in Real-World Settings From assembly lines to packaging machines, 24V PNP proximity sensors are the unsung heroes of automation. Their non-contact nature minimizes maintenance needs, as there’s no mechanical wear, and they excel in harsh conditions—think dust, moisture, or fluctuating temperatures. Here’s how they’re commonly used across industries:
One standout example is in food processing: 24V PNP sensors can detect metal contaminants in production lines without contaminating the product themselves, thanks to their stainless-steel housings and IP67-rated designs for water resistance.
Advantages and Why Choose 24V PNP Over Alternatives Selecting a 24V PNP proximity sensor offers distinct benefits that make it a go-to option. First, ease of integration—their output signals align directly with common PLC inputs, reducing wiring complexity and setup time. Compared to NPN sensors, PNP models provide a positive voltage when active, which often simplifies troubleshooting: if you see a voltage change, you know the sensor is working.
Second, they enhance system longevity. With no moving parts, 24V PNP sensors resist shock and vibration, lasting longer in high-impact environments. This translates to lower replacement costs and fewer unplanned stops. Additionally, their compatibility with the 24V standard means you can easily retrofit them into older systems, avoiding costly upgrades. For instance, a manufacturing upgrade might involve swapping outdated sensors for 24V PNP units, leading to a 20-30% improvement in detection accuracy, as reported in industry case studies.
What to Consider When Selecting a 24V PNP Proximity Sensor Not all proximity sensors are created equal, so making an informed choice is crucial. Start with the sensing range—ensure it matches your application needs (e.g., short-range for tight spaces or long-range for large equipment). Material compatibility is another factor: ferrous metals require inductive sensors, while plastics might need capacitive ones. Also, evaluate the environmental ratings; look for IP67 or higher to handle dust, water, or chemical exposure.
Installation is straightforward but demands attention to detail. Mount the sensor securely, avoid metallic obstacles that could cause false triggers, and use shielded cables for noise immunity. For maintenance, regular cleaning and signal checks—using a multimeter to verify the 24V output—can prevent failures. Remember, choosing a reputable supplier ensures compliance with ISO standards and access to technical support, which is vital for complex setups.
Addressing Common Queries and Troubleshooting Tips New users often ask: *How do I know if