check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
Imagine a bustling factory floor where robotic arms move with lightning speed, handling delicate components or operating in explosive environments. Traditional metal proximity sensors often fail here, succumbing to electromagnetic interference or spark risks. This is where fiber optic proximity sensors shine, offering a paradigm shift in safe, precise non-contact sensing. These innovative devices are rapidly becoming the go-to solution for demanding industries, harnessing the power of light transmitted through optical fibers to detect objects without physical touch.
So, what exactly is a fiber optic proximity sensor? At its core, it’s an optoelectronic system combining a light source (like an LED or laser), optical fibers, and a photodetector. The sensor emits modulated light through a fiber optic cable toward a target. Depending on the distance and reflectance properties of the object, the reflected or interrupted light signal travels back via the fiber to the detector, enabling accurate proximity detection. Unlike conventional inductive or capacitive sensors, this optical approach operates entirely without electrical components at the sensing point.

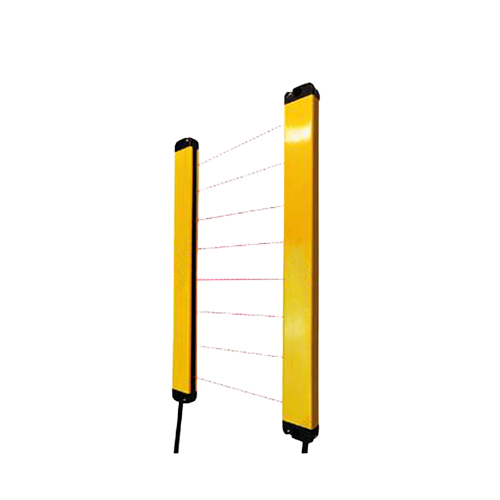
The operational principle is both elegant and robust. Light pulses travel through the optical fibers—thin, flexible strands of glass or plastic that act as conduits. When an object enters the detection zone, it alters the light beam’s intensity, phase, or reflection pattern. For example, in a reflectance-based setup, proximity is gauged by the strength of the return signal; closer objects reflect more light. Alternatively, through-beam variants use separate emitter and receiver fibers, detecting interruptions in the light path. This method achieves sub-millimeter precision under harsh conditions.
This technology offers compelling advantages that make it indispensable across sectors. First, it is inherently immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI), a critical feature in environments filled with motors or welding equipment. Second, the absence of electricity at the sensing tip eliminates spark hazards, enabling safe deployment in explosive atmospheres like oil refineries or chemical plants. Additionally, these sensors provide high resolution and fast response times, crucial for high-speed manufacturing lines. Their compact size and flexibility also allow installation in confined or geometrically complex spaces inaccessible to bulkier sensors.
The application scope for fiber optic proximity sensors is vast and growing. In industrial automation, they ensure precise positioning of robotic arms, monitor fill levels in tanks, or detect minute part misalignments on assembly lines. The automotive sector relies on them for quality control in painting or welding processes, leveraging their resistance to heat and fumes. Beyond factories, these sensors play vital roles in medical devices—such as monitoring catheter positions without radiation—and renewable energy systems, like tracking turbine blade movements. Their durability in extreme temperatures (-40°C to +150°C) and corrosive settings further expands their utility.
While initial investment costs can be higher than standard sensors, the long-term value is undeniable. Reduced downtime from EMI-related failures, minimal maintenance due to non-contact operation, and enhanced safety lead to significant savings. When implementing these systems, factors like fiber choice (glass for high temperature, plastic for flexibility) and proper alignment are crucial for optimal performance. Innovations in miniaturization and signal processing continue to drive down costs and boost capabilities, paving the way for broader adoption in smart cities, aerospace, and even consumer electronics.
As industries increasingly prioritize safety, precision, and resilience, the shift toward optical sensing is accelerating. Advances in material science promise even thinner, more sensitive fibers, while integration with IoT platforms enables real-time analytics and predictive maintenance. Whether navigating the complexities of Industry 4.0 or pioneering new frontiers in medical technology, fiber optic proximity sensors stand as a beacon of reliability. Their ability to transform light into actionable insights ensures they will remain at the forefront of non-contact detection solutions.