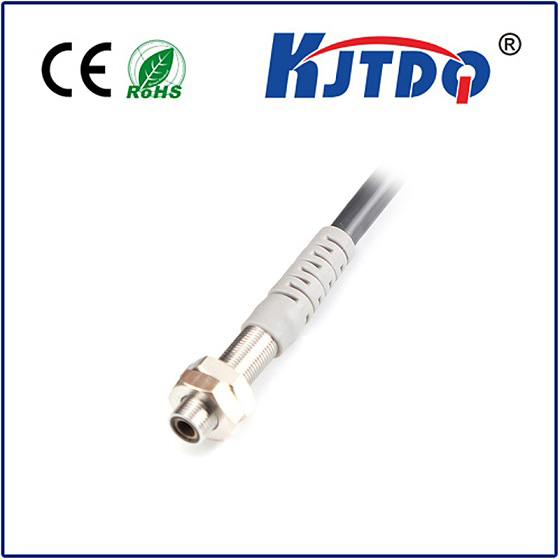
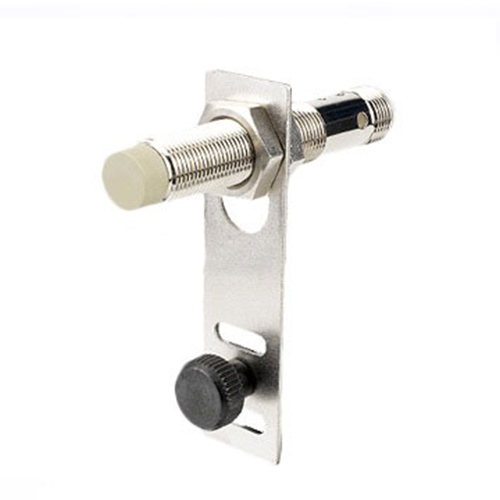
LDM-G Pull rope switch
- time:2025-09-24 00:04:54
- Click:0
LDM-G Pull Rope Switch: The Critical Lifeline for Conveyor Safety
Imagine a split-second incident on a fast-moving conveyor belt. A snagged piece of material, a worker’s clothing caught – disaster looms. In these critical milliseconds, the difference between a near miss and a catastrophic accident can hinge on one essential device: the LDM-G Pull Rope Switch. This specialized emergency stop mechanism isn’t just another piece of equipment; it’s the vital last line of defense, empowering personnel to halt dangerous machinery instantly from any point along its length. Understanding its function, importance, and the specific advantages of the LDM-G model is paramount for anyone responsible for industrial safety.
The Non-Negotiable Need for Emergency Stops
Conveyor systems are the workhorses of numerous industries – mining, aggregate processing, manufacturing, logistics, and power generation. While essential for efficiency, their moving parts and immense power pose significant entanglement, crushing, and impact hazards. Safety standards worldwide mandate accessible emergency stop devices (ESDs) on such machinery. The pull rope switch fulfills this requirement uniquely well, offering a continuous, easily accessible activation cable running parallel to the conveyor. Unlike fixed stop buttons located only at specific points, the pull rope allows an operator or bystander to trigger an emergency shutdown from virtually any location along the conveyor’s hazardous zone simply by pulling the rope.
How the LDM-G Pull Rope Switch Operates: Simplicity for Safety

The principle behind the LDM-G Pull Rope Switch is elegantly straightforward yet robust:
- The Rope: A durable, reinforced cable is installed along the conveyor’s full length, typically at waist height for easy access.
- The Switches: LDM-G units are installed at strategic intervals (typically 30-50 meters apart, depending on design standards). Each switch contains the critical activation mechanism.
- Activation: Pulling the rope in any direction applies lateral tension. This tension acts directly on the operating lever of the nearest LDM-G switch.
- Circuit Break: This movement instantly forces the switch to change state. Crucially, the LDM-G incorporates force-guided (positively driven) contacts. This means the mechanically linked contacts physically snap open, ensuring a positive break of the safety control circuit, regardless of weld or corrosion. This guaranteed opening is fundamental to safety integrity.
- Machine Shutdown: Breaking this safety circuit sends a signal to the conveyor’s motor control center (MCC), commanding an immediate and uncontrolled stop of the drive motor(s). It bypasses normal stopping sequences – safety demands halting motion now.
Why the LDM-G Model Stands Out: Engineered for Reliability
Not all pull rope switches are created equal. The LDM-G designation signifies specific design features crucial for harsh industrial environments and dependable safety performance:
- Rugged Construction: Built from robust materials like die-cast aluminum or reinforced polyamide to withstand impact, vibration, dust, and corrosion.
- High Ingress Protection (IP Rating): Typically rated IP67 or higher, meaning it’s highly resistant to dust ingress and can withstand immersion in water up to 1 meter deep for 30 minutes. This ensures reliability in dirty, wet, or washdown environments.
- Force-Guided Contacts: As mentioned, this is non-negotiable for safety-rated E-Stops. It guarantees contact separation and provides a clear “state” signal for monitoring systems.
- Double-Break Contacts: LDM-G switches often feature contacts that physically break the circuit in two places simultaneously, significantly increasing reliability and fault tolerance.
- Self-Monitoring Capability: Designed to allow integration with safety relays or controllers (PL e / SIL 3 capable systems) that can detect potential faults like welded contacts or broken internal springs, triggering an alarm if the switch itself is unsafe.
- Clear Visual Indication: Features like a highly visible, brightly colored actuator flag (often yellow) that clearly changes position (e.g., pops out) upon activation, providing immediate visual confirmation of the trip.
- Manual Reset: After activation, the switch must be manually reset at the device itself by an operator. This prevents automatic restarting and requires acknowledgment of the emergency situation before operations resume.
Key Applications: Where the LDM-G is Mission Critical
The LDM-G Pull Rope Switch is indispensable wherever long conveyors operate and personnel interact with or work near the belt line:
- Mining and Quarrying: Crucial along crusher feed conveyors, overland conveyors, and transfer points where rockfalls or blockages occur.
- Bulk Material Handling (Ports, Terminals, Power Plants): Essential for ship loaders/unloaders, stacker/reclaimers, and long coal/ore conveyors.
- Cement and Aggregate Production: Protecting workers near feeders, crushers, and material transfer conveyors.
- Recycling Facilities: Halting conveyors processing unpredictable material streams.
- Manufacturing and Warehousing: Along assembly line conveyors or large sorting/distribution systems.
Installation and Maintenance: Ensuring Peak Performance
Proper implementation is vital for the LDM-G to perform as intended:
- Mounting: Install switches securely at specified intervals per the design layout and relevant standards (like ISO 13850, ANSI B11.19, AS 4024.1). Ensure smooth rope travel with minimal friction.
- Rope Tension: Maintain correct initial tension. Too loose can cause slack and poor response; too tight can cause premature wear or false trips. Use tensioners or weights as specified.
- Alignment: Ensure the rope runs straight into the switch actuator at the correct angle to guarantee reliable tripping force.
- Wiring: Connect according to manufacturer diagrams directly into the safety-critical emergency stop circuit. Regular testing is mandatory! Conduct functional tests frequently (e.g., weekly/monthly) by pulling the rope at various points to verify activation and complete conveyor stoppage. Visually inspect ropes for wear, cuts, or corrosion, and check switch mechanisms for free movement. Actuator flags must be clearly visible. Document all tests and inspections diligently. Replacing worn components immediately is non-negotiable for safety integrity.