check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
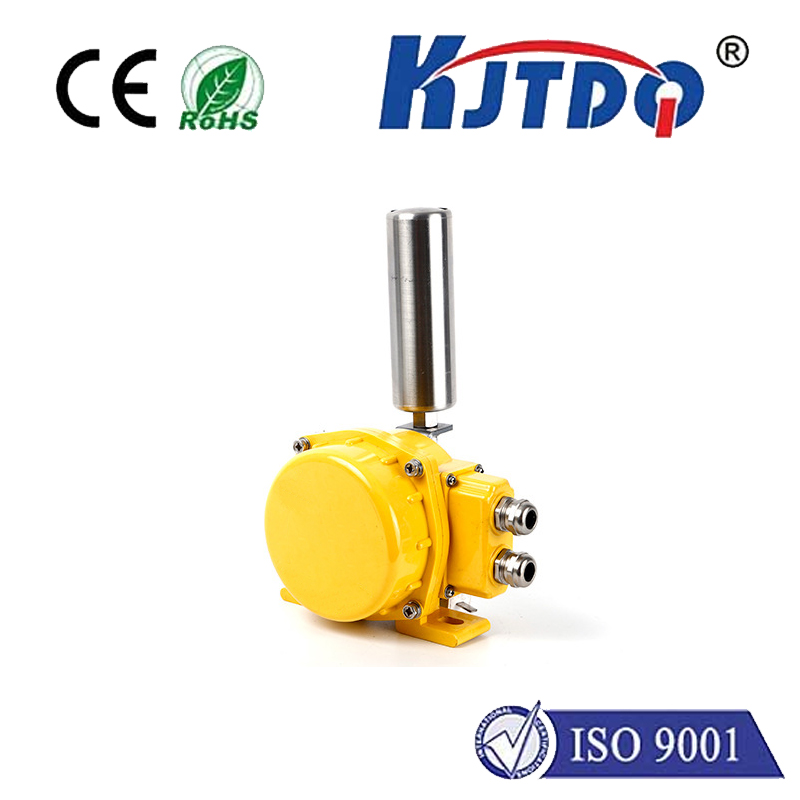
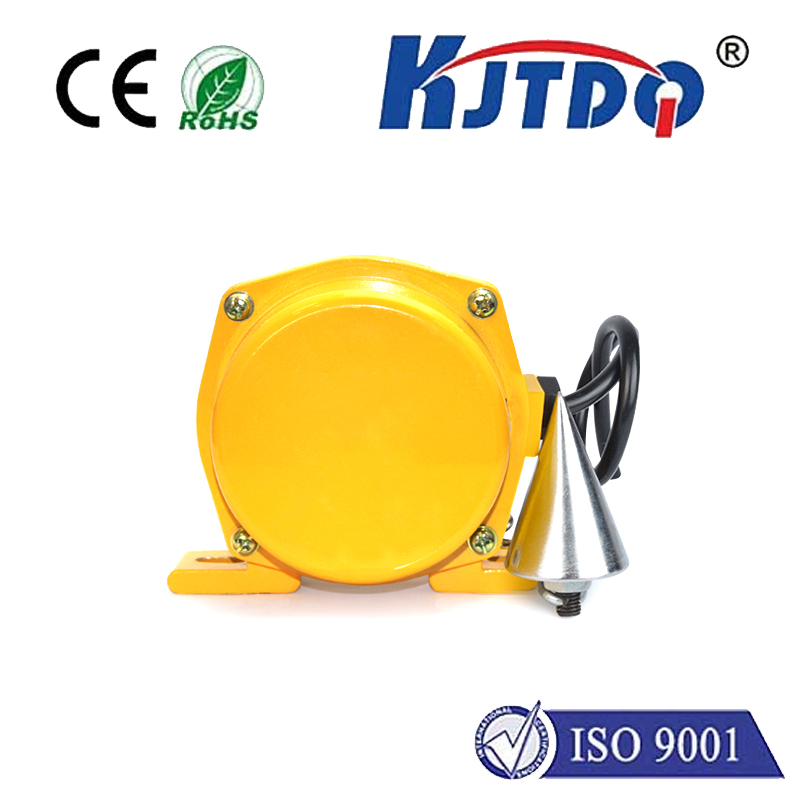
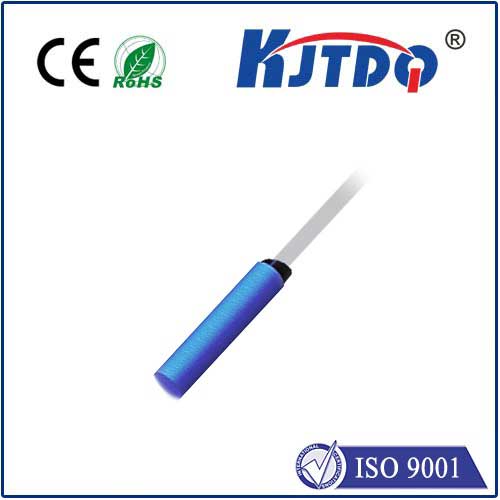
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, the demand for accurate and reliable detection systems has never been higher. Among the various solutions available, distance proximity sensors have emerged as a critical component in numerous applications, from industrial automation to consumer electronics. These sensors are designed to detect the presence or absence of objects within a specific range without any physical contact, offering a non-intrusive and efficient way to monitor environments and processes.
The fundamental principle behind distance proximity sensors involves emitting a signal, such as infrared light, ultrasonic waves, or laser beams, and measuring the time it takes for the signal to bounce back after hitting an object. This data is then processed to calculate the distance between the sensor and the object. One of the key advantages of this technology is its ability to provide real-time feedback, enabling systems to respond instantly to changes in their surroundings. For instance, in manufacturing plants, these sensors can be used to ensure that robotic arms maintain a safe distance from human workers, thereby enhancing workplace safety.
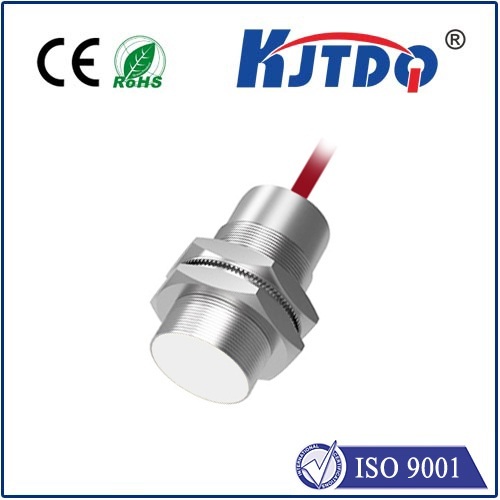
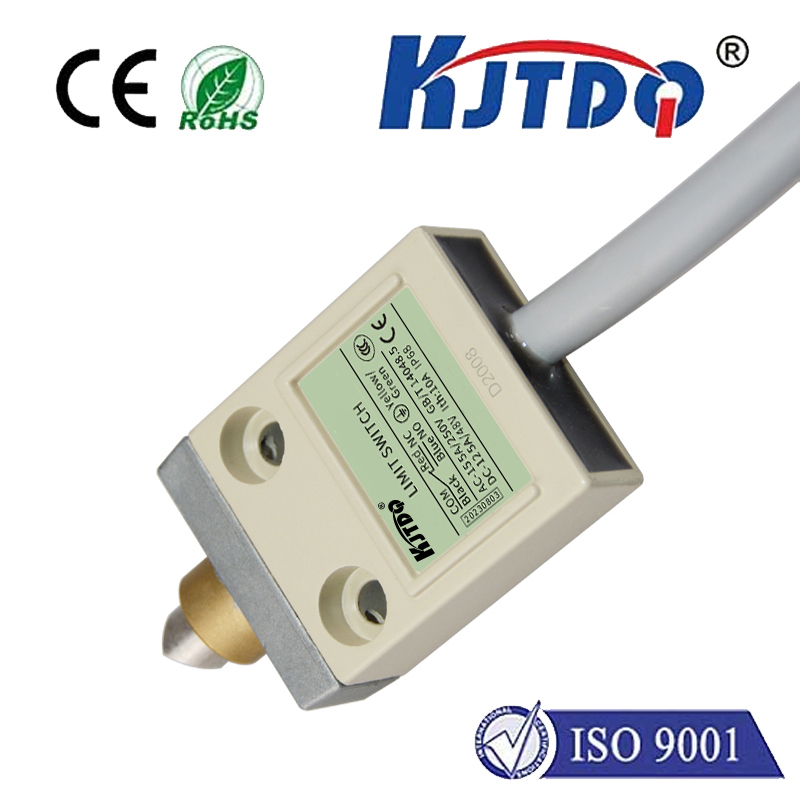
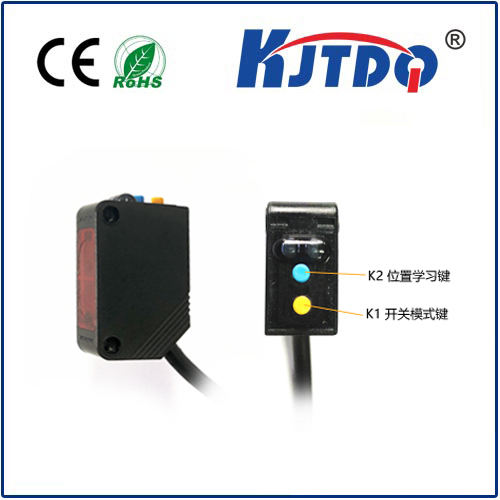
Moreover, distance proximity sensors are highly versatile and can be customized to suit different requirements. They come in various types, including inductive, capacitive, and photoelectric sensors, each with its own set of characteristics and ideal use cases. Inductive sensors, for example, are particularly effective for detecting metallic objects, making them suitable for automotive assembly lines. On the other hand, capacitive sensors can detect both metallic and non-metallic materials, which is useful in food processing industries where hygiene and contamination prevention are paramount.
In the realm of consumer electronics, distance proximity sensors play a crucial role in enhancing user experience. Smartphones, for instance, utilize these sensors to detect when the device is held close to the ear during a call, automatically turning off the display to prevent accidental touches. Similarly, in home automation systems, these sensors can trigger lights to turn on or off based on the presence of individuals in a room, contributing to energy efficiency and convenience.
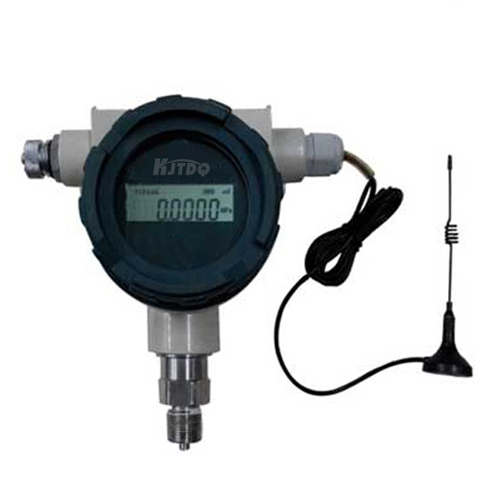
The integration of distance proximity sensors with Internet of Things (IoT) platforms has further expanded their capabilities. By connecting sensors to cloud-based systems, data can be analyzed and utilized for predictive maintenance, inventory management, and even smart city initiatives. For example, in parking garages, sensors can monitor available spaces and relay this information to drivers via mobile apps, reducing traffic congestion and saving time.
Despite their numerous benefits, selecting the right distance proximity sensor requires careful consideration of factors such as range, accuracy, environmental conditions, and cost. It is essential to evaluate the specific needs of an application to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance and calibration are also necessary to maintain accuracy over time, as factors like dust, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical wear can affect sensor readings.
Looking ahead, advancements in sensor technology are expected to drive further innovation. Developments in miniaturization, power efficiency, and artificial intelligence integration will likely lead to even more sophisticated detection systems. As industries continue to embrace automation and smart technologies, distance proximity sensors will remain at the forefront, enabling safer, more efficient, and intelligent operations across various sectors.